Anaerobic Digestion Types
There are many different anaerobic digestion types available in the markets that vary in process configurations and operating conditions. The design considerations and operating conditions of these treatment trains may be suitable for a particular type of feedstock or feedstocks mix but may not be applicable or economical for others. That is why digester type and technology should be selected based on the indented feedstock’s characteristics and availability (the amount to be treated) as well as desired output and process economy in mind.
Different Anaerobic Digestion Types:
These different anaerobic digestion types based on their feed type, operating conditions and process configuration can be classified into five different groups:
- Anaerobic Digestion based on Digester's Feeding Mode
- Anaerobic Digestion for Enhancing Solid Loading and Digestate Recirculation
- Anaerobic Digestion based on Feedstock's Solid Content
- Anaerobic Digestion based on Digester's Operating Temperature
- Anaerobic Digestion based on Digester's Stages and Reactor Configuration
A brief discussion of these different types are as follows:
Anaerobic Digestion based on Digester's Feeding Mode
Continuous Feed Digester
Continuous feed digesters are either feed continuously or semi-continuously. These are the most common type of digesters.
Batch Feed Digester
In Batch feed digesters, feedstocks are loaded in the digester and left there for a certain period for digestion to take place. Usually the batch digesters need to be bigger in volume due to the long retention time.
Anaerobic Digestion for Enhancing Solid Loading and Digestate Recirculation
Extended Solids Retention (ESR) Digestion
The Extended Solids Retention (ESR) digestion process has greater solids retention time (SRT) than the Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT). This is done by thickening the digestate via thickening equipment and then recycling it back to the digester. This process allows for a longer SRT than the HRT as the solids have been separated from the water and reintroduced to the digester. This extended SRT increases solid reduction and generates more biogas.
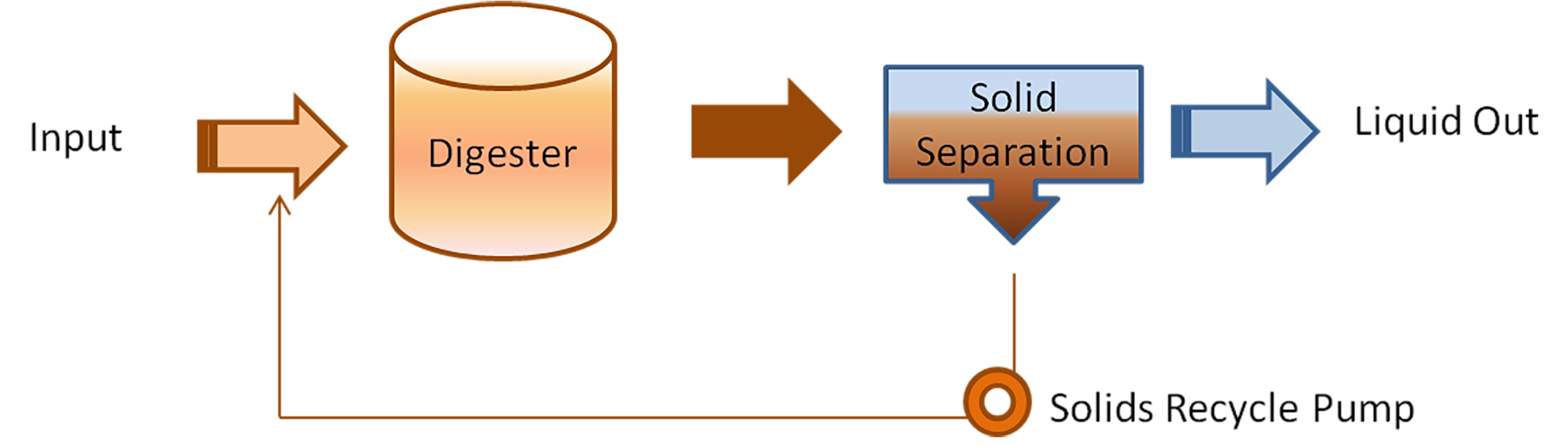
An Extended Solids Retention (ESR) Digestion Configuration (Data Source: WEF, 2004)
Some advantages and disadvantages of this process, as listed in the WEF white paper on the anaerobic digestion (2004) are:
Advantages:
- Decreased Anaerobic digester volume
- Extended organic conversion to methane
- Potential for reduction in overall polymer usage because of recycling
- Reduced digester volume requirements may result in lower life cycle cost
- Separating the SRT from the HRT provides greater flexibility in solids removal
- Increased solids concentration in the dewatering feed may result in improved dewatering
Disadvantages:
- Additional thickening equipments
- Added complexity
- The added
capital and operating cost for the additional thickening equipment.
Discover more anaerobic digestion technologies and digesters configuration in the following links:
Anaerobic Digestion based on Feedstock's Solid Content
Anaerobic Digestion based on Digester's Operating Temperature
Anaerobic Digestion based on Digester's Stages and Reactor Configuration
Find more on different Anaerobic digestion types here.
Discover more on Anaerobic Digestion and Biogas
Go back to the Eco Ambassador Home
Total Visits to Site:
