Biogas Purification!
The
primary objective of biogas purification is to remove biogas components like H2S,
water vapour, NH3, particles, etc. These components not only cause
environmental hazard and processing problems but also dilute the energy density
of biogas. The major contaminants of biogas and their related removal
technologies are discussed as follows:
Major Contaminants and related Biogas Purification Technologies:
Water Vapor:
Biogas generated from anaerobic digestion is usually saturated with water vapor. Water vapour may condense into water or ice and thus result in corrosion and clogging issues. Most biogas utilization processes require relatively dry gas, so removal of water vapor is required.
- Passive cooling: Biogas pipe line is run though underground for a short period of time. Water condenses from the biogas as it cool down. The condensate either discharges to sewer or recycle back.
- Refrigeration and Pressurization: Heat exchangers can be used to cool down the biogas so that the water vapour gets condensed. Biogas can be further pressurized to dry it more.
- Absorption: Biogas can be passed
through drying medium like glycol, hygroscopic salts, silica gel, aluminum oxide
etc. to absorb water. These drying medium can be regenerated by drying them at
high temperature and sometime at high pressure as well. Eventually the drying
media has to be replaced.
Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S):
H2S is a toxic and corrosive gas and its concentration in raw biogas may vary based on the feedstock. H2S in biogas has to be reduced to harmless level to protect the downstream processes and equipments as well as toxicity to human health.
- Water scrubbing: Biogas is feed from the opposite direction of water flow to create a solution of H2S in water. The water can be regenerated and scrubbing water discharged can be reduced.
- Activated Carbon: Biogas is fed through an activated carbon filter which removed sulphides by adsorption. Activated carbon media can be regenerated.
- Iron Hydroxide or Oxide: Biogas is led through a media composed of woodchips and iron oxide or hydroxide. H2S is removed as iron oxides react with sulfides (H2S) to produce iron sulfide. Bed can be regenerated several times before requiring replacement.
- Biofiltration: Biofiltration uses microbes living on a packed medium to remove sulfides. Sulfides in the biogas get absorbed into a liquid film and are then metabolized by the microbial cells. It is available as above grade packed towers or below grade systems, filled with natural media like wood chips or peat moss.
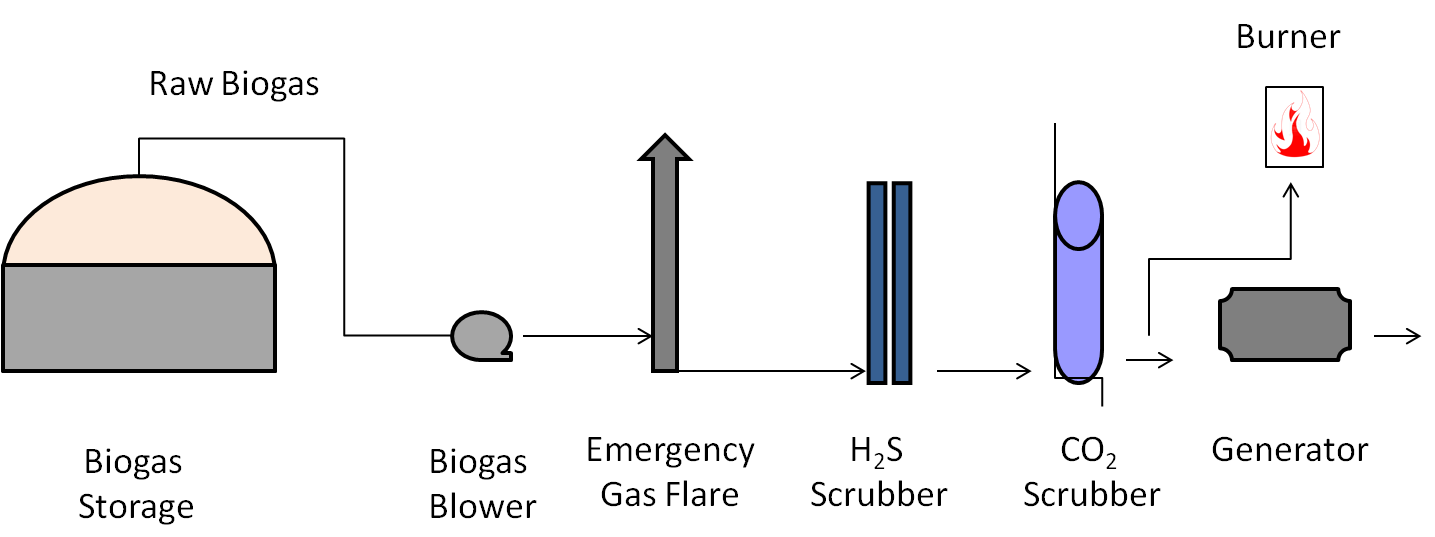
A simplified Biogas Purification Diagram
Ammonia: Ammonia can cause corrosion to the downstream process equipments. It can also form nitrogen oxides (NOx) from the combustion of biogas. Ammonia is soluble in water, so it can be removed using the following two methods:
- Water Scrubbing
- Refrigerated water vapour removal methods
Particles:
Sometimes
dust and oil particles from the compressors may be present in the biogas.
- Filter: The particles in the biogas can be removed by using filter of 2 to 5μm size. These filters need to be replaced in regular interval as part of maintenance.
Siloxanes:
The
presence of siloxanes in biogas cause abrasive siloxane deposits on equipments
and reduce their life significantly.
- Silica gel: Silica gel has good potential of removing of certain siloxane compounds from biogas. It has High adsorption capacity.
- Cooling: Siloxanes can be removed from the cooled gas with condensation water.
- Activated carbon: Activated carbon removes siloxane from biogas via adsorption.
Halogenated
hydrocarbons:
Halogens
can cause corrosion to mechanical parts of the plant. They can also form
dioxins and furans during combustion of biogas.
-
Activated carbon:
Activated carbon can be used to remove halogenated hydrocarbons.
References
- Anaerobic Digestion Guideline by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of British Columbia (BC), Canada.
- Petersson, A. and Wellinger, A., (2009); Biogas Upgrading Technologies –Developments and Innovations, by IEA Bioenergy.
- Biogas Processing for Utilities, American Biogas Council
Discover more on Biogas Purification!
Go to Biogas Utilization!
Go to the Eco Ambassador Home!
Total Visits to Site:
